Introduction:
Navigating the Shifts in Japan’s Leadership and Monetary Future
As the curtains rise on the Liberal Democratic Party’s presidential race, the impending departure of Prime Minister Kishida Fumio heralds a new era of leadership in Japan. Investors and market analysts await with bated breath the economic policies the new premier will enact and the potential ramifications these policies may have on the Bank of Japan’s monetary strategy.
The Heat of the Election:
The Stiff Competition in LDP’s Presidential Race
The race for the LDP crown is a frantic scramble with a plethora of candidates vying for the top spot. A recent survey, conducted between September 13th to 15th by Nikkei News and Tokyo TV, has thrown the race wide open, with no clear frontrunner in sight. The poll suggested a three-way near deadlock among former LDP Secretary-General Shigeru Ishiba, Minister in charge of Economic Security Sanae Takaichi, and political scion Shinjiro Koizumi.
Market Sentiments:
The Anticipation of New Economic Directives
Market sentiment is largely governed by the expected economic and financial policies of the LDP leadership contender who will claim victory. The election methodology, which equally weights the votes from LDP members across prefectures and LDP Diet members, only adds to the suspense of the outcome.
Candidates’ Influence:
Diverse Backgrounds, Unique Vision
Shigeru Ishiba, leveraging his experience as Japan’s former defense minister, mounts his fifth attempt for LDP leadership. Sanae Takaichi, the spotlight-loving female contender, makes her second attempt after her defeat to Kishida in the previous race. Meanwhile, political ‘rising star’ Shinjiro Koizumi banks on his lineage with the endorsement from former Prime Minister Suga Yoshihide.

The Central Bank Equation:
Speculating the New Prime Minister’s Stance
Investors speculate over the new prime minister’s potential influence on the Bank of Japan’s interest rates, especially after Takaichi’s nod towards maintaining lower rates. Despite exiting negative interest rate policies in March and undergoing a rate hike up to 0.25%, the Bank of Japan faces growing inflation pressures justifying additional rate increases.
Currency Dynamics:
The Yen in the Global Market
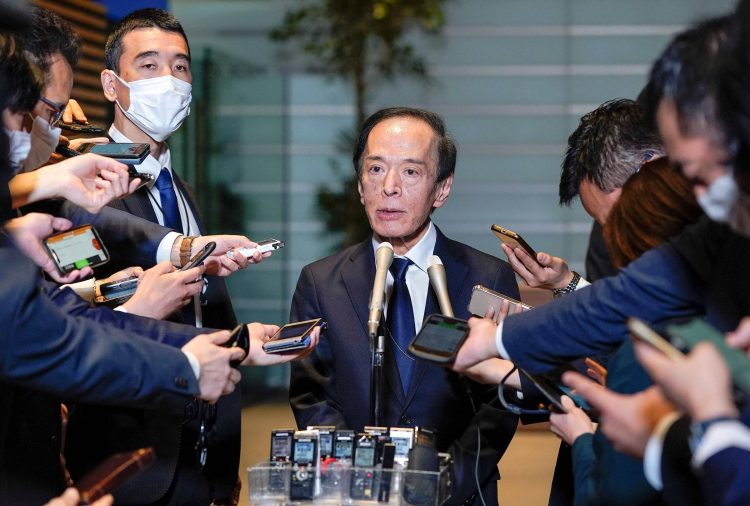
A recent surge in the yen and subsequent market discussions, including those by BOJ board member Nakagawa Junko hinting at further rate hikes congruent with inflation trends, spell a period of potential financial market volatility. BOJ’s Executive Director Tamura Naoki’s comments indicate that future rate hikes could potentially exceed current economic forecasts, positioning the neutral policy rate at 1% or higher.
Market Reactions:
The Central Bank’s Balancing Act
Amid the policy shifts and market stirrings, the new Japanese leadership’s vision for national economic stewardship and their approach to central bank policy are under intense scrutiny. The BOJ’s interest rate adjustments, interlaced with market stability, forecast inflation, and economic growth, are central to this financial saga. While the BOJ is likely to hold steady in its September meeting, the economic discourse anticipates further interest rate hikes by year-end.