The global economic landscape is experiencing a transformative shift, with emerging trade blocs taking center stage. These alliances, often driven by regional proximity and shared economic interests, are redefining traditional trade patterns, creating new economic powerhouses, and challenging the dominance of established global economies. This article explores the rise of emerging trade blocs, their impact on the global economy, and the opportunities and challenges they present for stakeholders worldwide.
The Rise of Emerging Trade Blocs
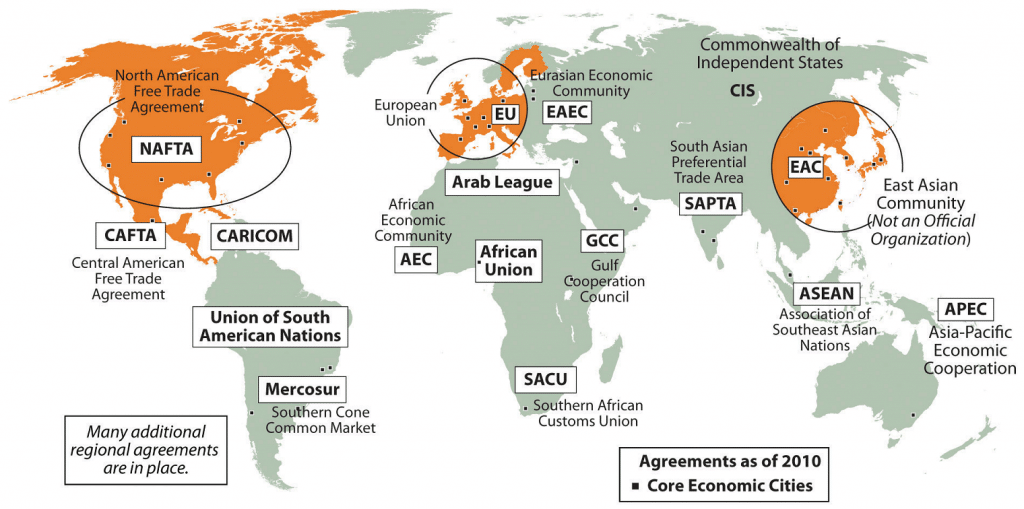
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
One of the most significant developments in global trade is the establishment of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). Comprised of 15 Asia-Pacific nations, including China, Japan, South Korea, and the ASEAN countries, RCEP is the world’s largest trade agreement by GDP and population. The pact aims to reduce tariffs, streamline trade regulations, and enhance economic integration among member countries.
African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA)
Another notable bloc is the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which seeks to unify Africa’s fragmented markets. AfCFTA includes 54 of the 55 African Union nations, making it the largest free trade area by member states. By eliminating tariffs on 90% of goods, the agreement aims to boost intra-African trade and foster industrialization across the continent.
Mercosur and Latin America’s Growing Unity
In Latin America, Mercosur continues to be a cornerstone of regional economic cooperation. With Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay as its founding members, Mercosur focuses on facilitating trade and promoting political stability. Recent talks of expanding partnerships with external regions indicate a growing ambition to assert Latin America’s presence on the global stage.
Challenging Traditional Economic Hegemony
Shifting Power Dynamics
The emergence of these trade blocs signifies a shift in global power dynamics. Historically dominated by Western economies and institutions such as the WTO, IMF, and World Bank, the global trade landscape is now witnessing the rise of new economic centers. For instance, RCEP’s formation underscores the increasing influence of Asia-Pacific countries, particularly China, in global trade.
Decline of Unilateralism
Emerging trade blocs also mark a move away from unilateralism and bilateral agreements. By fostering multilateral cooperation, these blocs emphasize collective bargaining power, enabling smaller economies to negotiate on more equal terms with global superpowers.
Impact on Global Trade Flows
Trade Diversification
Emerging trade blocs encourage diversification of trade flows by reducing dependency on traditional markets. For instance, African nations, through AfCFTA, are now focusing on intra-continental trade rather than relying heavily on exports to Europe or North America.
Enhanced Market Access
By eliminating trade barriers, these blocs provide businesses with access to larger markets. This not only boosts export opportunities but also attracts foreign direct investment (FDI) as companies seek to leverage the benefits of expanded regional integration.
Supply Chain Reconfiguration
The rise of trade blocs necessitates the reconfiguration of global supply chains. Companies are increasingly looking to establish regional supply chains within trade bloc territories to capitalize on reduced tariffs and logistical efficiencies. This trend is particularly evident in RCEP countries, where intra-regional trade is expected to flourish.
Opportunities for Stakeholders
Businesses
For businesses, emerging trade blocs offer immense opportunities to tap into new markets, reduce operational costs, and diversify supply chains. Companies operating in manufacturing, agriculture, and technology stand to benefit the most from streamlined trade regulations and expanded customer bases.
Governments
Governments within trade blocs gain increased leverage in international negotiations. By pooling resources and aligning policies, member states can collectively address economic challenges, attract investments, and enhance regional stability.
Consumers
Consumers also benefit from trade blocs through lower prices, improved product quality, and greater variety. The elimination of tariffs and competition among suppliers drive innovation and cost efficiency, ultimately favoring end-users.
Challenges and Criticisms
Economic Disparities
One of the primary challenges facing emerging trade blocs is addressing economic disparities among member states. In AfCFTA, for example, less developed nations may struggle to compete with stronger economies, potentially exacerbating inequality within the bloc.
Regulatory Harmonization
Harmonizing regulations across diverse economies is another significant hurdle. Differences in legal frameworks, labor standards, and environmental policies can impede seamless integration, delaying the realization of trade bloc benefits.
Geopolitical Tensions
Trade blocs are not immune to geopolitical tensions. Conflicting national interests, power struggles, and external influences can disrupt cooperation and undermine the effectiveness of these alliances.
Long-term Implications
Redefining Global Trade Norms
Emerging trade blocs are poised to redefine global trade norms by prioritizing regional cooperation over global consensus. This shift could lead to a more fragmented yet dynamic global trade environment, where regional agreements play a pivotal role in shaping economic policies.
Environmental and Social Considerations
The focus on economic growth within trade blocs must be balanced with environmental sustainability and social equity. Incorporating green policies and inclusive development strategies will be crucial for ensuring long-term success.
Future of Multilateralism
The rise of trade blocs raises questions about the future of multilateral institutions like the WTO. While these blocs promote regionalism, they also highlight the need for a robust global framework to address issues that transcend regional boundaries, such as climate change and digital trade.
Conclusion
Emerging trade blocs are reshaping the global economy in profound ways. By fostering regional integration, enhancing trade flows, and challenging traditional economic hegemonies, these alliances are creating new opportunities and redefining the rules of global commerce. However, they also face significant challenges that require careful navigation to ensure equitable and sustainable growth. As the world continues to evolve, the success of these trade blocs will depend on their ability to adapt, innovate, and foster collaboration in an increasingly interconnected global landscape.



































